Product Category

TEL: +86-13927455531
Email: sales@passive-rfid-tags.com
Radio-frequency identification(RFID)
What is RFID?
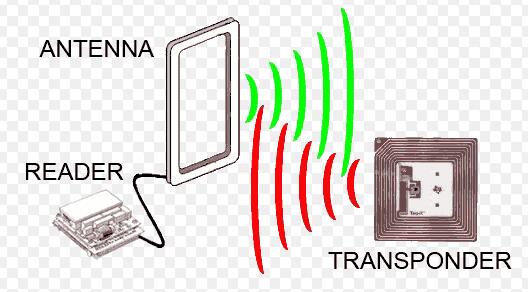
Radio frequency identification, or RFID, is a generic term for technologies that use radio waves to automatically identify people or objects. There are several methods of identification, but the most common is to store a serial number that identifies a person or object, and perhaps other information, on a microchip that is attached to an antenna (the chip and the antenna together are called an RFID transponder or an RFID tag). The antenna enables the chip to transmit the identification information to a reader. The reader converts the radio waves reflected back from the RFID tag into digital information that can then be passed on to computers that can make use of it.
What is automatic identification?
Automatic identification, or auto ID for short, is the broad term given to a host of technologies that are used to help machines identify objects. Auto identification is often coupled with automatic data capture. That is, companies want to identify items, capture information about them and somehow get the data into a computer without having employees type it in. The aim of most auto-ID systems is to increase efficiency, reduce data entry errors and free up staff to perform more value-added functions, such as providing customer service. There is a host of technologies that fall under the auto-ID umbrella. These include bar codes, smart cards, voice recognition, some biometric technologies (retinal scans, for instance), optical character recognition (OCR) and radio frequency identification (RFID).
RFID frequency and read range
RFID systems can be broken down by the frequency band within which they operate: low frequency, high frequency, and ultra-high frequency. There are also two broad categories of RFID systems-passive and active. In the sections below we will explore the frequencies and types of RFID systems.
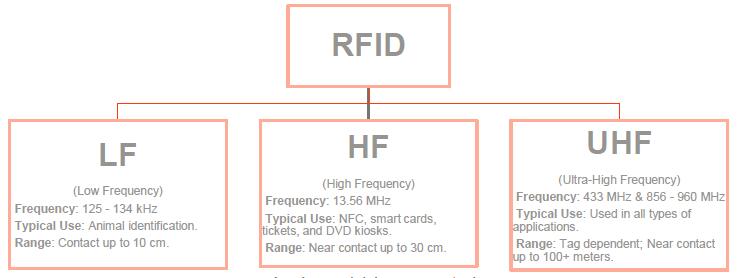
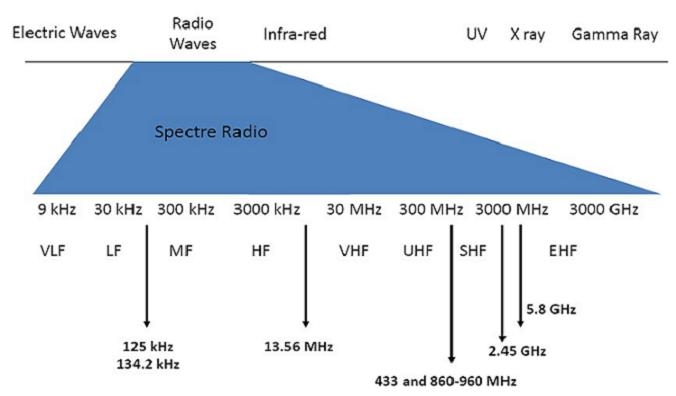
Within the UHF Frequency range of 856 – 960 MHz, there are two primary subsets:
a) The FCC (US) standard frequency range of 902-928 MHz
b) The ETSI (EU) standard frequency range of 865-868 MHz
The FCC standard is used throughout North America as well as the majority of the Caribbean and much of South America. The ETSI standard is used throughout the European Union and most countries adhering to EU standards. Various other subsets within the above ranges are used throughout the world. If you are planning on deploying RFID Equipment in a particular country, but aren’t sure of that country’s standards, then we can assist in providing the appropriate frequency range.